CMBE – A New ACRF Data Product for Climate Studies
Submitter:
Xie, Shaocheng — Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Area of research:
Cloud Distributions/Characterizations
Journal Reference:
Science
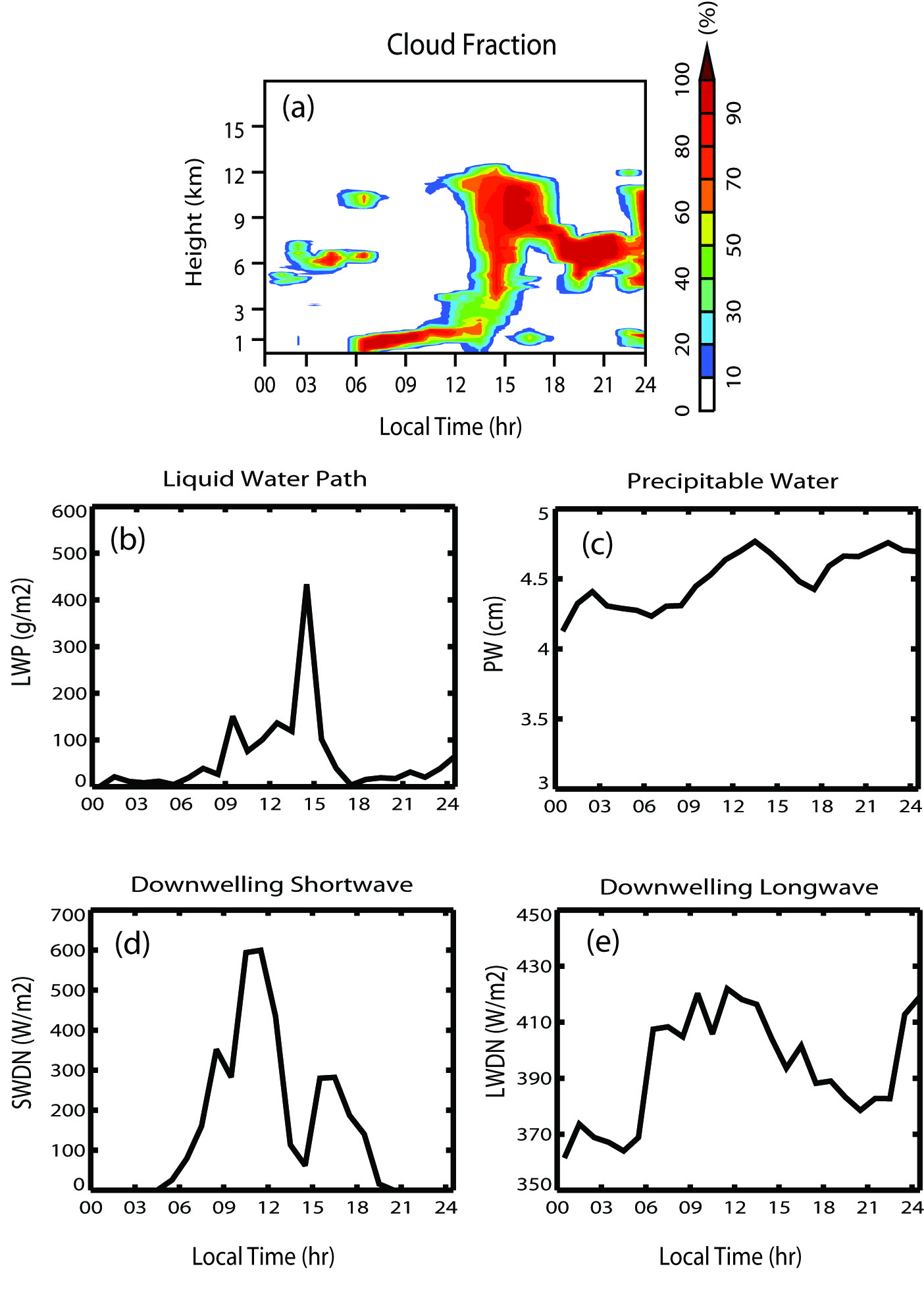
Long-term continuous ACRF data provide invaluable information to improve our understanding of the interaction between clouds and radiation and an observational basis for model validation and improvement and for climate studies. To facilitate use of ACRF data in climate studies, ARM has developed a new integrated data product, named the “Climate Modeling Best Estimate (CMBE),” for the climate community. This new data product assembles those quantities, which are both well observed by ACRF over many years and often used in model evaluation, into one single data set with a temporal resolution (one hour) comparable to a typical resolution used in climate model output.
Impact
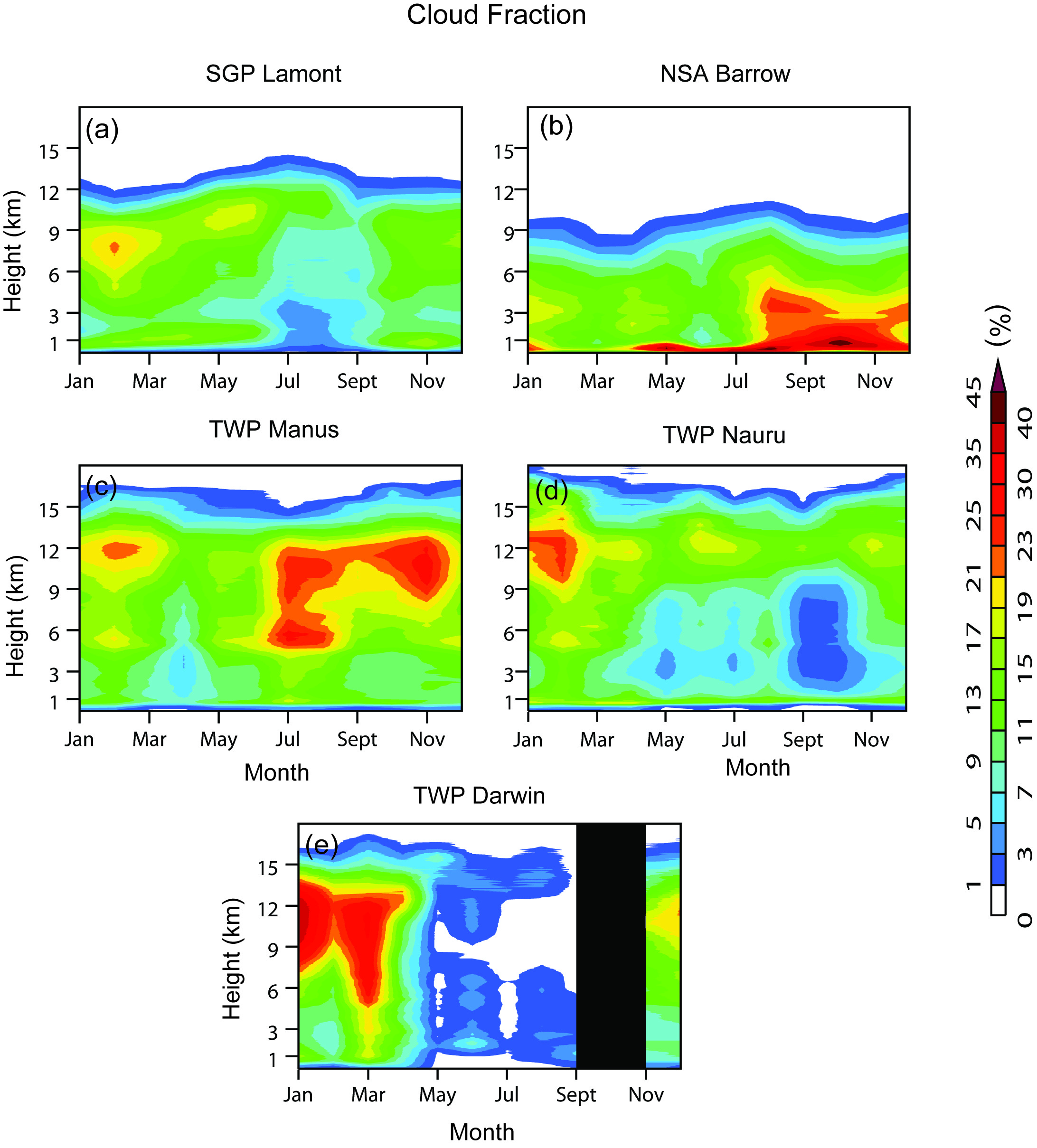
A short article describing the CMBE data product has been accepted recently for publication in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society (BAMS). In the paper, the authors discussed the potential value of CMBE data for climate studies. By providing a few examples, they clearly demonstrated the usefulness of CMBE data in studies of cloud processes, diurnal and seasonal variability, climate change, and climate model evaluation (see the attached figures).
Summary
The current CMBE data set contains cloud fraction, cloud liquid water path, column precipitable water, and surface radiative fluxes for all five ACRF permanent research sites — the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Lamont site; the North Slope of Alaska (NSA) Barrow site; and the Tropical Western Pacific (TWP) Manus, Nauru, and Darwin sites — over the periods where ACRF data are available. For SGP, the large-scale state variables from radiosondes and model analysis, top-of-the-atmosphere (TOA) radiative fluxes, surface turbulent fluxes, surface precipitation, and other surface meteorological fields are also available. Since its initial release in February 2008, the new data product has quickly drawn the attention of the climate community. It is being used for model evaluation by two major U.S. climate modeling centers, the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL).