Cloud Condensation Nuclei Vertical Profile Data Product Updated
Published: 14 November 2022
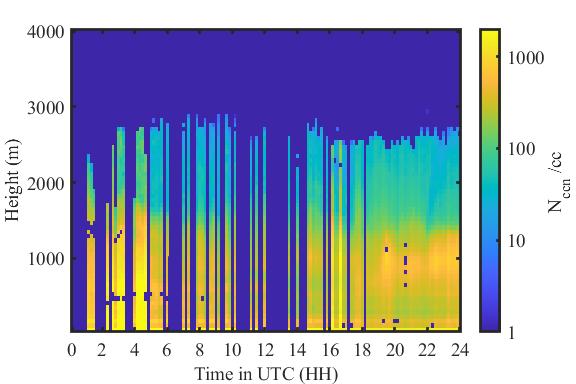
A new version of the Retrieved Number concentration of Cloud Condensation Nuclei value-added product (RNCCN VAP) is now available for evaluation. This VAP provides the vertical distribution of cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) number concentrations for better representation of aerosol indirect effects in climate models.
New in RNCCN is the use of a hygroscopicity parameter (gamma) based on the Hänel (1976) parameterization to calculate extinction changes due to hygroscopic growth of aerosol. Hygroscopicity is the ability of a particle to take up moisture from the environment and is important for understanding the variation in lidar-derived extinction with altitude.
RNCCN gives users the vertical profiles of CCN concentrations at the various supersaturation values measured by the CCN particle counter. (Supersaturation occurs when the relative humidity is at least 100%.) RNCCN also routinely provides measurements of CCN near cloud base, which is a proxy for the aerosol that is entrained into clouds and leads to droplet formation.
For input, the VAP uses quality-controlled Raman lidar profiles (aerosol extinction and feature mask) and CCN spectral data in addition to the hygroscopicity data.
Calculated from Raman lidar and interpolated sonde data, the new gamma parameter is applied only in the well-mixed boundary layer. The use of the gamma parameterization will enable running the VAP at more locations and over more time periods.
Output data are filtered using atmospheric stability and aerosol feature tests. The aerosol feature test filters lidar data that have been labeled as a cloud and/or rain. The VAP performs calculations only when aerosol is detected. Profiles associated with large values (>5) of gamma are not calculated.
RNCCN evaluation data are available from January 16 to December 31, 2016, for the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility’s Southern Great Plains Central Facility near Lamont, Oklahoma. This data set allows for comparisons with in situ CCN data from the 2016 Holistic Interactions of Shallow Clouds, Aerosols, and Land-Ecosystems (HI-SCALE) field campaign at the Southern Great Plains atmospheric observatory.
The RNCCN data have 1-hour time resolution and 60-meter vertical resolution. Data are in netCDF format.
More information about RNCCN can be found on the VAP web page.
To provide feedback or ask questions about the evaluation data, please contact VAP science mentor Gourihar Kulkarni, VAP developer Chitra Sivaraman, or ARM aerosol translator John Shilling.
Access the RNCCN data set in the ARM Data Center. (Go here to create an account to download the data.)
To cite the data, please use doi:10.5439/1813858.
Reference
Hänel G. 1976. “The Properties of Atmospheric Aerosol Particles as Functions of the Relative Humidity at Thermodynamic Equilibrium with the Surrounding Moist Air.” Advances in Geophysics, 19: 73–188, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60142-9.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















