Observations and simulations of shallow convective post-frontal clouds over the Southern Ocean
Submitter
Geerts, Bart — Department of Atmospheric Science, University of Wyoming
Area of Research
Cloud Processes
Journal Reference
Hu Y, Z Lebo, B Geerts, Y Wang, and Y Hu. 2023. "Vertical Structure and Ice Production Processes of Shallow Convective Postfrontal Clouds over the Southern Ocean in MARCUS. Part II: Modeling Study." Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 80(5), 10.1175/JAS-D-21-0272.1.
Hu Y, B Geerts, M Deng, C Grasmick, Y Wang, C Lackner, Y Hu, Z Lebo, and D Zhang. 2023. "Vertical Structure and Ice Production Processes of Shallow Convective Postfrontal Clouds over the Southern Ocean in MARCUS. Part I: Observational Study." Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 80(5), 10.1175/JAS-D-21-0243.1.
Science
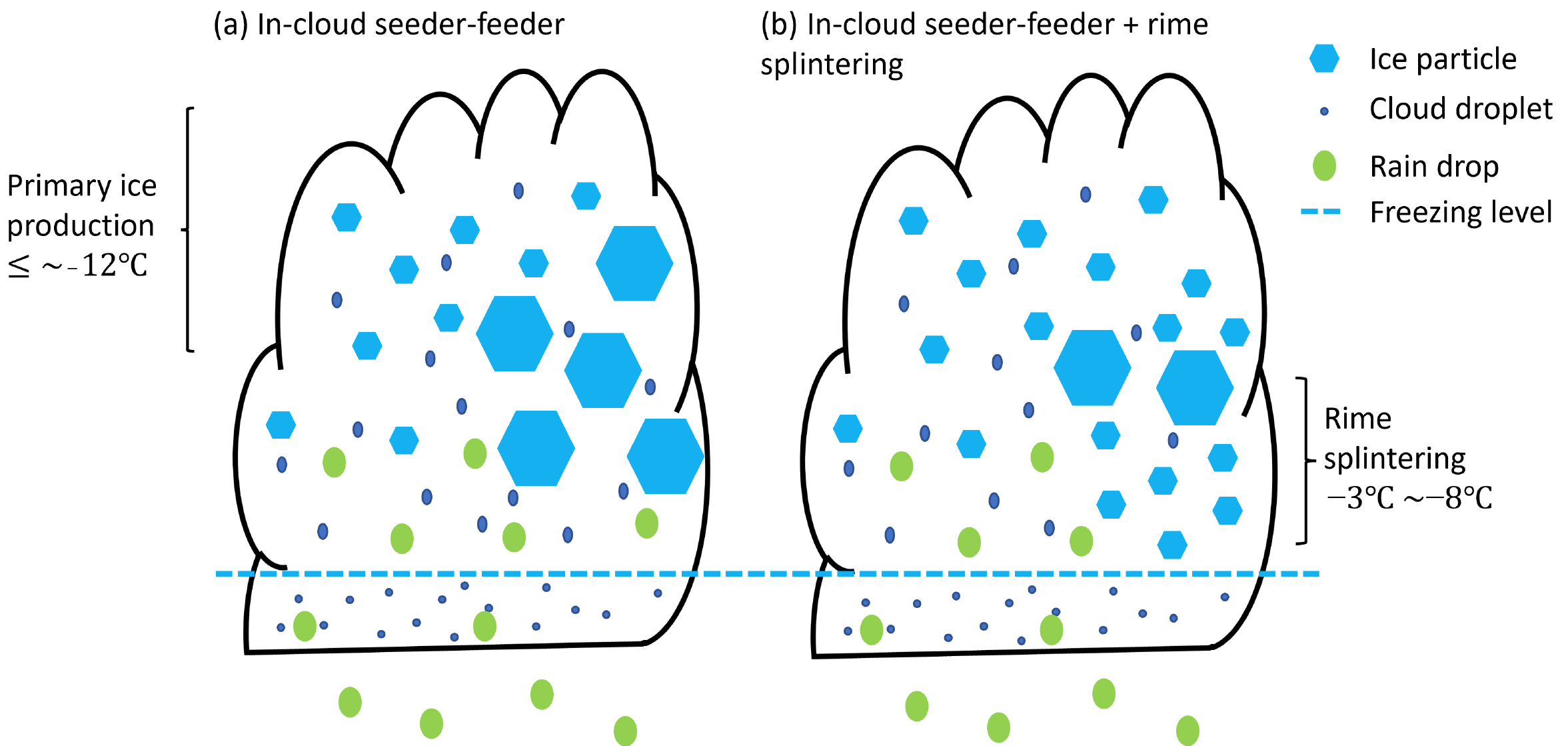
Figure 1. Schematic of the effects of primary ice production process only (left), and both primary ice production process and active rime splintering process (right) on ice particles. From journal.
Climate models generally predict a lower albedo than observed over the Southern Ocean, and this is largely attributed to a low cloud bias, especially in the post-frontal cold sector of midlatitude cyclones. This in turn may be due to an excess of ice in these simulated clouds, resulting in rapid precipitation fall-out and an overly brief cloud lifespan. The objective of this observational and modeling study is to examine whether shallow post-frontal clouds over the Southern Ocean are dominated by supercooled drops, or by snow and ice.
Impact
It is extremely difficult to quantify cloud phase, ice water content, and ice particle size distributions from remote sensors.
Summary
We find that these clouds contain much supercooled liquid, even though cloud-top temperatures generally are rather cold (around –18 °C to –8 °C). This may be attributable to the extremely low concentration of ice nucleating particles in this environment. The numerical experiments call for more observations of ice nucleating particles, especially over the remote Southern Ocean.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















