Oliktok Point, Alaska, KAZR data set available for mixed-phase cloud studies
Submitter:
Williams, Christopher R — University of Colorado Boulder
Area of research:
Cloud Processes
Journal Reference:
Science
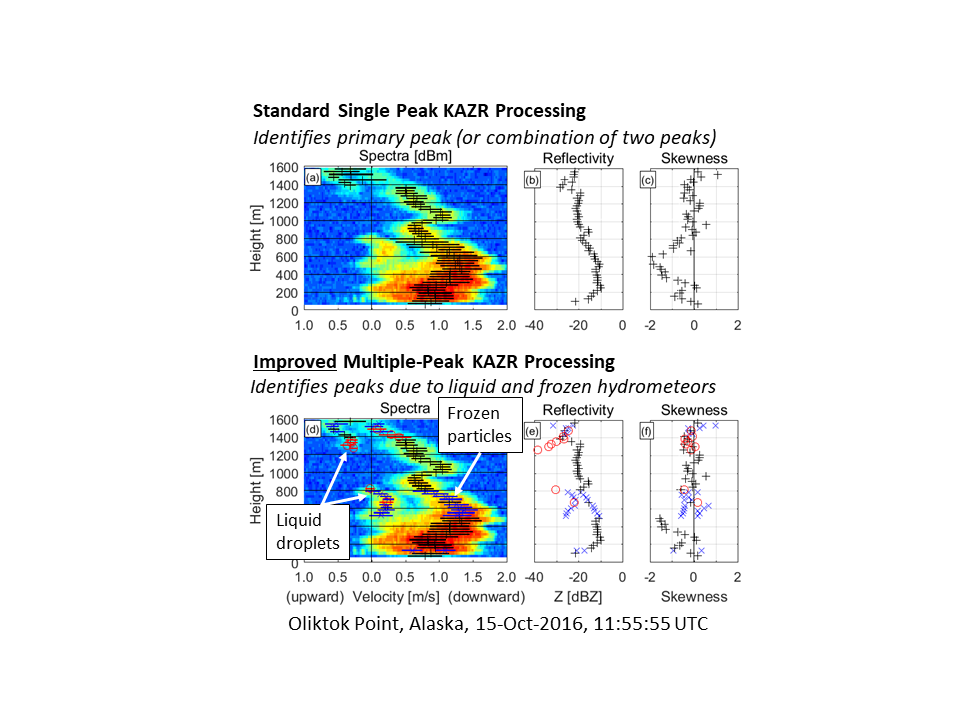
Two years of KAZR spectra from Oliktok Point, Alaska, have been processed to classify spectral peaks used to identify liquid and frozen hydrometeor populations within mixed-phased clouds. High-order spectral moments (including velocity spectrum skewness and kurtosis) were estimated for each spectrum peak and are available for download from the DOE ARM Data Center for 2016 and 2017.
Impact
Isolating two or more spectral peaks in KAZR velocity spectra is needed to identify the occurrence of “mixed-phase clouds”, which is when liquid and frozen hydrometeors occur simultaneously in the same cloud. Spectral moments estimated from standard ARM spectral-processing routines only estimate low-order moments and are misleading because they assume a single hydrometeor population is producing the observed velocity spectrum. New mixed-phase cloud studies are now possible by ARM/ASR scientists with this new multiple-peak, high-order moment data set.
Summary
The DOE ARM facility deployed a 35-GHz vertically pointing radar (called KAZR, for Ka-band ARM Zenith-pointing Radar) at Oliktok Point, Alaska, as part of the ARM’s third Mobile Facility (AMF3). Due to buildings and other nearby structures, ground clutter is a significant issue in the recorded KAZR Doppler velocity spectra. Since standard ARM processing algorithms cannot distinguish ground clutter from atmospheric signals, the first part of this study developed a clutter mitigation methodology to remove ground clutter from the Doppler velocity spectra before estimating spectral moments. The second part of this study developed a method to classify spectral peaks used to identify liquid and frozen hydrometeor populations contributing to the KAZR Doppler velocity spectra. These two hydrometeor populations occur simultaneously in mixed-phase clouds and produce multiple-peaked spectra. The last part of this study estimated high-order moments (including velocity skewness and kurtosis) for each identified peak as well as for the simplified assumption of a single peak. Observations from 2016 and 2017 have been processed and are available to the ARM/ASR community from the ARM Data Center (https://iop.archive.arm.gov/arm-iop/0pi-data/williams/).