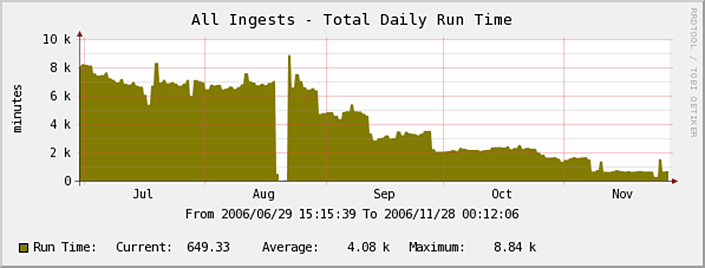
Scientific instrumentation at the ARM sites generates massive amounts of data for atmospheric research. These data are processed at the Data Management Facility (DMF) housed at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. In late 2006, the DMF completed the replacement of its database processing capabilities with a new Data System Database (DSDB), after a 2-year process of incremental upgrades and migration of metadata. The final upgrade showed significant improvement by increasing datastream processing up to 120 times faster.
Since nearly the outset of the ARM Program more than 15 years ago, the DMF relied on an internal “technical database” to store the datastream definitions (field names and attributes) and configurations used in processing ARM data. The technical database was implemented to provide storage of simple keyword/values. While functional, the technical database had room for improvement in performance, security, and especially in capability. In 2004, ARM data infrastructure staff began working to replace the technical database with a modern database using PostgreSQL. The new database engine was chosen because of its maturity and full featured database capabilities, as well as its open-source licensing features which simplifies distribution to the various remote ARM sites.
The DSDB was designed to logically and efficiently store the configuration and status information previously stored in the technical database. In order to retire that database, every datastream ingest needed to be re-released and tested with the new database-a process that was completed in October 2006. After installing a copy of the DSDB at the data reprocessing center at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the ARM Archive reported a 120-fold increase in performance on long-running jobs. The effort to replace the technical database and develop the DSDB has yielded dramatic results—particularly in improved ingest run times—and provides maximum processing capacity for data system growth.